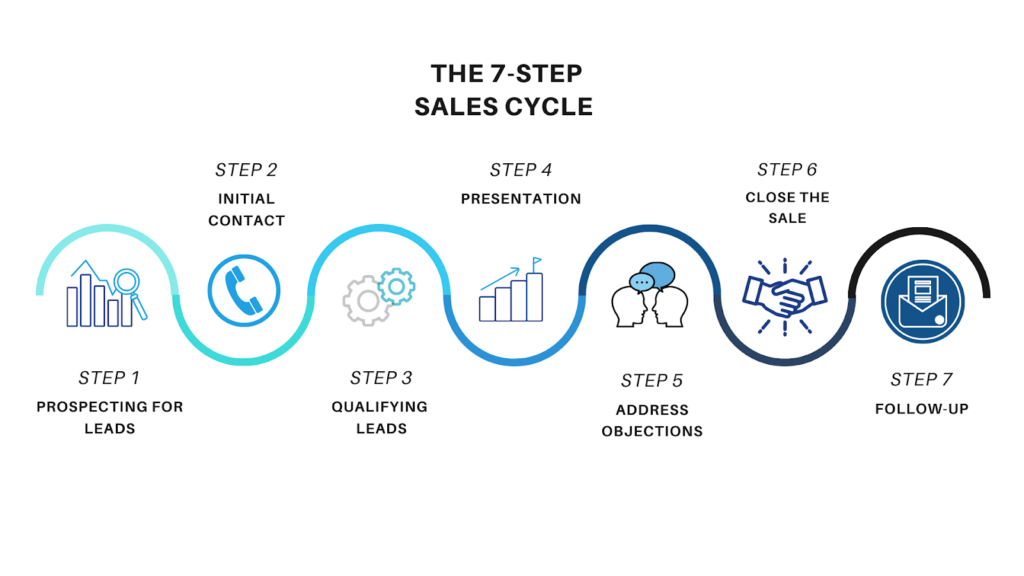
The sales cycle is a series of predictable phases that salespeople follow to turn prospects into customers. It is crucial because it provides a structured approach to selling, helping businesses streamline their processes and increase sales efficiency. Understanding the sales cycle allows sales teams to identify where prospects are in their buying journey and tailor their approach accordingly.
Stages of the Sales Cycle
Prospecting: This stage involves identifying potential customers who may be interested in your product or service. Techniques include networking, cold calling, and using social media platforms. Effective prospecting tools, such as CRM systems and lead databases, help in finding and managing potential leads. Incorporating sales tips, like personalizing outreach and following up consistently, can significantly improve prospecting success.
Initial Contact: Making the first move to connect with a prospect is critical. This can be done through emails, phone calls, or face-to-face meetings. Best practices include personalized communication and clear value propositions to capture the prospect’s interest.
Qualification: Not all leads are equal, so qualifying them is essential. This involves assessing if the lead has a genuine need for the product, the budget to buy it, and the authority to make purchasing decisions. Tools like BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline) can be useful in this stage.
Presentation: This stage is where the sales pitch happens. It involves demonstrating how the product or service meets the prospect’s needs. Customizing the presentation to address specific pain points and using compelling visuals can significantly enhance its effectiveness.
Handling Objections: Prospects often have concerns or objections. Common objections revolve around price, product fit, or competition. Active listening and addressing these concerns directly and empathetically can turn objections into opportunities.
Closing the Sale: This is the critical moment of securing the deal. Closing techniques vary, but recognizing buying signals and making it easy for the prospect to say yes are key. Techniques like the assumptive close, the urgency close, and the summary close are commonly used.
Follow-Up: After closing the sale, following up is vital for maintaining customer relationships. This can include thank you emails, onboarding assistance, and periodic check-ins. Effective follow-up ensures customer satisfaction and opens opportunities for upselling and referrals.

Types of Sales Cycles
B2B Sales Cycle: Business-to-business sales cycles are typically longer and more complex, involving multiple decision-makers and higher transaction values.
B2C Sales Cycle: Business-to-consumer sales cycles are usually shorter, with fewer decision-makers and lower transaction values. The buying process is often more emotionally driven.
Sales Cycle Management
Effective management involves monitoring and measuring the sales cycle’s performance. CRM tools are essential for tracking interactions and progress. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like conversion rates, sales cycle length, and customer acquisition cost are used to gauge effectiveness.
Optimizing the Sales Cycle
Identifying bottlenecks and streamlining processes are crucial for optimization. Leveraging data analytics helps in understanding patterns and making informed decisions. Automation tools can also speed up repetitive tasks, allowing sales teams to focus on high-value activities.
Sales Cycle and Customer Experience
A well-managed sales cycle enhances customer experience by providing timely and relevant interactions. Building trust and loyalty through personalized engagement leads to repeat business and positive referrals. Case studies of successful sales cycles often highlight the importance of customer-centric approaches.
Challenges in the Sales Cycle
Common challenges include handling objections, managing long sales cycles, and adapting to changing market conditions. Solutions involve continuous training, adopting new technologies, and staying agile to market trends.
Future Trends in Sales Cycle
Technology, such as AI and machine learning, is set to revolutionize sales cycles by providing deeper insights and automating tasks. Evolving customer expectations demand more personalized and seamless experiences. Future predictions include increased reliance on data-driven strategies and omnichannel engagement. Incorporating a sophisticated business phone system into this mix can further enhance the ability to meet these expectations by enabling more effective communication channels that integrate seamlessly with other digital platforms, offering a more cohesive customer experience.
Conclusion
Understanding the sales cycle’s intricacies is vital for any sales-driven organization. By following a structured approach and continually optimizing processes, businesses can improve their sales performance and build lasting customer relationships.
Appendices
A glossary of terms and additional resources can provide further clarity and support for sales teams. Templates and checklists offer practical tools for implementing effective sales strategies.
References
Books, articles, and websites provide further reading and insights into the sales cycle, helping to expand knowledge and expertise in this critical area of business.